Ion Sources
NEOMAFIOS
An external ECR ion source using 10 GHz microwaves and a permanent-magnet (NdFeB) mirror field. It supplies beams to the AVF cyclotron. It is used for generating light ions, offering stable operation and ease of handling.
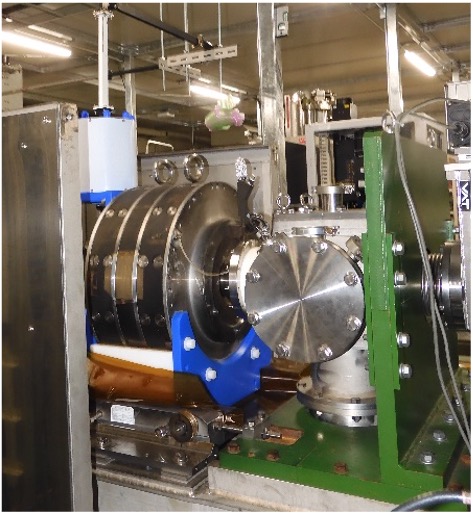

Fig. NEOMAFIOS.
| ECR ion source | |
| RF frequency | 10 GHz |
| Mirror magnet | Permanent magnet (Fe–Nd–B) |
| Vacuum chamber | Diameter 67 mm, length 170 mm |
| Pumping speed | 520 l/s |
| Extraction voltage | 5–50 kV |
| Available ions | p, d, He, Li–Mg, Ar |
HIPIS
A polarized ion source developed to generate high-intensity, high-polarization proton and deuteron beams.
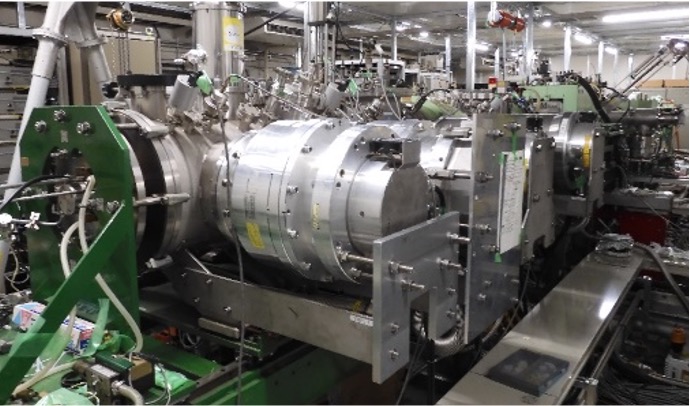
Fig. HIPIS.
| High-intensity polarized ion source | |
| Dissociator | RF (13.6 MHz, 300 W), nozzle (20 K+N2), Skimmer (Diameter: 4 mm) |
| Sextupole | Permanent magnet (Nd–B–Fe, NEOMAX-35H) |
| RF transition unit | Two weak-field and two strong-field RF transition units |
| ECR ionizer | RF (52.45 GHz, 200 W) + Solenoid + N2 |
| Extraction voltage | 5–20 kV |
| Ion supply | pol-p, pol-d |
SCECR
A superconducting ECR (Electron Cyclotron Resonance) ion source using 18 GHz microwaves to efficiently generate high charge-state ions. The superconducting magnets provide strong, stable fields, enabling high-intensity beams across elements from light to medium-heavy.

Fig. SCECR.
| Superconducting ECR ion source | |
| RF frequency | 18 GHz |
| Magnet system | Superconducting coils (mirror magnetic field) + permanent magnet hexapole |
| Typical extraction voltage | 5–30 kV |
| Available ions (examples) | He–Ar, Kr, Xe (light to medium-heavy elements) |
Accelerators
K140 AVF Cyclotron
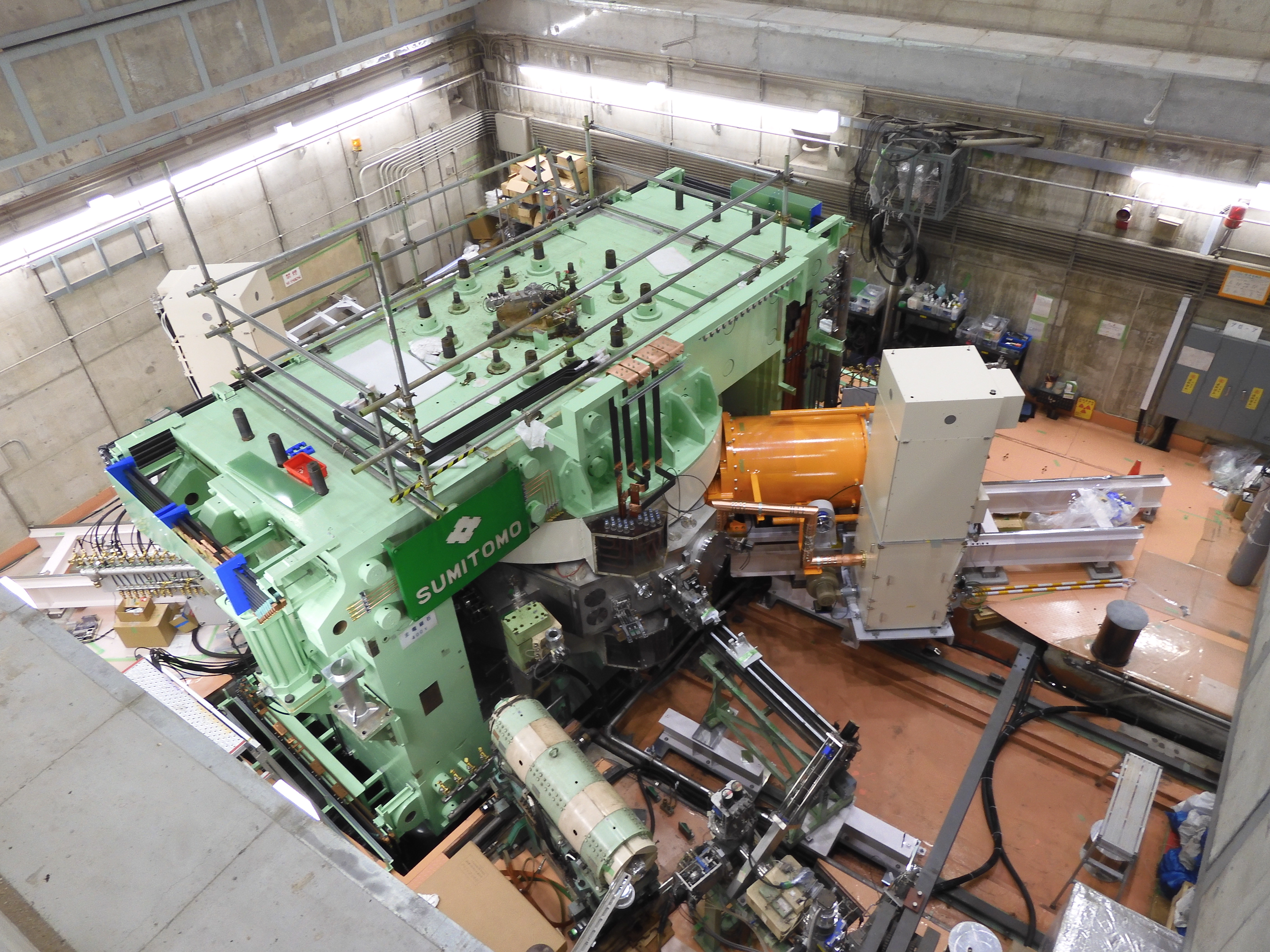

| Magnet | |
| Pole diameter | 3300 mm |
| Pole gap | 206–347 mm |
| Isomagnetic field | 1.6 T |
| Extraction radius | 1000 mm |
| Trim coils | 16 pairs |
| Valley coils | 3 pairs |
| Weight | 400 tons |
| Acceleration system | |
| Dee electrode | Double type with 87° spanning angle |
| Resonator | Coaxial; movable shorting plate |
| Frequency | 18–36 MHz |
| Maximum accelerating voltage | 60 kV |
| Harmonics | 1, 2, 3, 6 |
| Extraction | Electrostatic deflector |
K400 Ring Cyclotron

| Magnet | |
| Sector magnets | 6 |
| Pole gap | 60 mm |
| Maximum field | 1.75 T |
| Trim coils | 36 pairs |
| Injection radius | 2 m |
| Extraction radius | 4 m |
| Weight | 2200 tons |
| Acceleration | |
| Single-gap cavities | 3 |
| Frequency | 30–52 MHz |
| Harmonics | 6, 10 |
| Maximum accelerating voltage | 500 kV |
| RF power | 250 kW / cavity |
| Flat-top cavity | |
| Single-gap | 1 |
| FT harmonic | 3 |
| Frequency | 90–156 MHz |
Old K140 AVF Cyclotron

| Magnet | |
| Pole diameter | 3300 mm |
| Pole gap | 206–347 mm |
| Isomagnetic field | 1.6 T |
| Extraction radius | 1000 mm |
| Trim coils | 16 pairs |
| Valley coils | 3–5 pairs |
| Weight | 400 tons |
| Acceleration system | |
| Dee electrode | Single type with 180° spanning angle |
| Resonator | Coaxial; movable shorting plate |
| Frequency | 6–19 MHz |
| Maximum accelerating voltage | 60 kV |
| Harmonics | 1, 3 |
| Extraction | Electrostatic deflector; weak-focusing magnetic channel |
Available Beams
* Black: achievements with the old AVF cyclotron (beam delivery requires acceleration tests).
* Red: achievements with the AVF cyclotron updated in 2021 (acceleration tests not required).
| Ion | Energy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charge State | AVF | AVF+RING | ||
| AVF | RING | (MeV) | (MeV) | |
| 1H | 1+ | 1+ | 10–80, 25, 44, 65 | 100–392, 416, 230, 392 |
| 1H2 | 1+ | 1+ | 56 | 140 |
| 2H | 1+ | 1+ | 10–56 | 80, 103, 140, 200 |
| 3He | 1+ | 14, 25 | ||
| 3He | 2+ | 2+ | 45, 73,88 | 300, 420 |
| 4He | 1+ | 10 | ||
| 4He | 2+ | 2+ | 38–130, 28.5, 87, 100 | 210, 300, 400 |
| 6Li | 2+ | 40, 45 | ||
| 6Li | 2+ | 3+ | 73, 82 | 309, 360 |
| 7Li | 3+ | 3+ | 110, 150 | 455 |
| 11B | 3+ | 69 | ||
| 11B | 5+ | 5+ | 200 | 900 |
| 12C | 4+ | 80, 105, 110, 164, 85 | ||
| 12C | 4+ | 6+ | 145 | 600 |
| 12C | 5+ | 250 | ||
| 12C | 5+ | 6+ | 262 | 1200 |
| 13C | 5+ | 6+ | 178 | 780 |
| 14N | 5+ | 7+ | ||
| 15N | 6+ | 7+ | 220 | 975 |
| 16O | 5+ | 100–170 | ||
| 16O | 6+ | 190 | ||
| 16O | 6+ | 8+ | 286 | 1280 |
| 18O | 4+ | 90, 106, 100 | ||
| 18O | 5+ | 118, 135, 165 | ||
| 18O | 6+ | 165, 246 | ||
| 18O | 6+ | 8+ | 246 | 1080 |
| 18O | 7+ | 8+ | 322 | 1440 |
| 19F | 4+ | 100 | ||
| 20Ne | 6+/7+/8+ | 155, 300 | ||
| 22Ne | 6+ | 130, 190 | ||
| 22Ne | 8+ | 10+ | 254 | 1100 |
| 22Ne | 8+ | 10+ | 400 | 1760 |
| 24Mg | 5+ | 140 | ||
| 36Ar | 11+ | (16+) | 437 | 1872 |
| 40Ar | 8+ | 200 | ||
| 40Ar | 11+ | 360, 374 | ||
| 40Ar | 12+ | 17+ | 486 | 2060 |
| 86Kr | 21+ | 640 | ||
| 86Kr | 23+ | 731 | ||
| 132Xe | 24+ | 897 | ||


